dutch strengths
The unique combination of Dutch strengths
Revolutionizing drug development to boost health, innovation & affordability starts in the Netherlands
In the Netherlands, the life sciences & health sector joins forces to shape the future of drug development. Good collaborations between all parties involved is essential for progress, including academia, industry, government, patients, health care providers, health foundations and insurance companies. Together they pioneer smart solutions all along the drug development chain that boost health, innovation and affordability.
Instrumental to success is the unique combination of Dutch strengths:
- Entrepreneurship
A fertile breeding ground for start-ups and SMEs - Research infrastructure
Collaboration in the quadruple helix - Science
Great science is our backbone - Quality of life
Life is good in the Netherlands, for life sciences and beyond - Location and logistics
The Gateway to Europe
The Netherlands is the place to be to develop & deliver innovative healthcare solutions faster and better from bench to bedside!
Watch the video below to get an the strenghts of the Dutch Life Sciences & Health sector.

Cyclomics: Winner of the Venture Challenge Fall 2017
At the Dutch Life Sciences Conference 2017, Chrétien Herben, director of the LifeSciences@Work Accelerator, announced Cyclomics as winning team of the 18th edition of the Venture Challenge. The start-up Cyclomics has developed a technology to measure cancer recurrence in liquid biopsies, by detection of cancer mutations in blood at single-molecule sensitivity. This way the start-up aims to improve the survival rate for many different types of cancer.
According to the Venture Challenge jury the technological innovation of Cyclomics addresses worldwide challenges in the field of early cancer diagnosis. The team presented this high potential technology via an excellent venture plan and Q&A.
Each year millions of people die from cancer, often due to recurrent disease. To prevent recurrent cancer from becoming untreatable it should be detected as early as possible. The technology of Cyclomics addresses this burning clinical need by offering detection of cancer mutations in blood at single-molecule sensitivity, which is not reached by any other liquid biopsy test on the market. Moreover, Cyclomics provides a comprehensive test as it can detect mutations in complete genes or gene panels, ensuring secondary tumors or newly emerging tumor clones are not missed. This technology can become the first cancer diagnostic test that can be combined with portable third-generation sequencing, providing low-cost access to any diagnostic laboratory worldwide.
"Our ambition is to market our Cyclomics technology for different indications and target groups, starting with the diagnosis of head-and-neck cancer. In this way we hope to improve survival of many cancer patients worldwide," states Wigard Kloosterman, Principal Investigator, cancer genomics, University Medical Center Utrecht.
The Venture Challenge Fall 2017 started in September this year and came to an end during the Dutch Life Sciences Conference 2017 in Oss. Other participating teams were UPyTher, Breath Medics, Excoris, MarkMyGenes and PlatformFive. Participating in the Venture Challenge leads to clear venture plans, as well as to very well-prepared and presented pitches. The LifeSciences@Work Accelerator is powered by Health~Holland, Top Sector Life Sciences & Health.
Contact Wigard Kloosterman for more information about Cyclomics.
New Call open: join the Venture Challenge Spring 2018!
Our specialised coaching focuses on developing your initial idea into a solid business case during an entrepreneurial approach with boot camps, 1-on-1 coaching and mentoring. Startup teams learn to identify key risks, analyse customer value propositions, develop a validation strategy, learn to build a venture plan and learn how to get connected. Read more at the LifeSciences@Work website. Application deadline: 5 March 2018.

Launch of new innovation label Briskr strengthens the Nijmegen region
Since the 12th of October the Nijmegen region is enriched with Briskr, Health and High Tech Generator. This strong collaboration of Triple Helix parties improves the Life Sciences, Health & High Tech ecosystem. Briskr streamlines the variety of support programmes for startups and SMEs. Even more, Briskr puts the Nijmegen region and its unique climate on the map. Briskr picks up on the strong developments and natural strengths of the regional Health & High Tech sectors.
“The direct reason for this collaboration is the diverse landscape of innovation-stimulating initiatives. By bundling these activities, we offer the ecosystem better support activities and we can strengthen the Health & High Tech industry,” says Rikus Wolbers, programme manager of Briskr.
Briskr Academy
John Schalken is manager Business Support. He is, among other things, responsible for the Briskr Academy. “The Briskr Academy offers a coherent package of workshops, coaching and consultations hours and other business development related activities. Entrepreneurs can enroll and improve their skills in fields like financial management, subsidies, intellectual property or product creation. It’s possible to sign up once, or to follow a complete series of activities.”
Shared use of facilities
One of the big advantages of the Briskr consortium is the possibility to use the available know-how and facilities. All the network partners grant access to their specific knowledge, equipment and other facilities. According to Rikus Wolbers this is very important because businesses often are not aware of the possibilities the knowledge institutions and research facilities can offer.
“Bridging the gap between science and business is one of our main fields of attention and stimulation. There are beautiful opportunities to enroll research project on the campuses of Radboud University, Radboud University Medical Centre and HAN University of Applied Sciences. We are going to highlight these possibilities and connect the parties proactively.”
About the Briskr consortium
Parties active in the so-called triple helix founded Briskr. The main partners are the Municipality of Nijmegen, Health Valley Netherlands, Kadans Science Partner, Novio Tech Campus, East Netherlands Development Agency (OostNL), the Province of Gelderland, Radboud University, Radboud University Medical Centre (Radboudumc) and SMB Life Sciences. Associate partners like Business Cluster Semiconductors, Rabobank Rijk van Nijmegen and The Economic Board enrich these parties. On October 12th Briskr has been launched during an event revolving around ‘Impact on Health & High Tech’ with the former mayor of Eindhoven, Rob van Gijzel.
Source: Novio Tech Campus

Orkambi included in the basic healthcare package
Former Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport, Edith Schippers, has decided to include the medicine Orkambi for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in the basic healthcare package. This is great news for the CF patients in need of Orkambi. After a period of uncertainty, Schippers finally made this decision because she was able to reach an agreement on the price with Vertex. Part of this price agreement with the manufacturer is that the details of the agreement remain confidential.
Former Minister Schippers: “I am incredibly happy for the patients that the negotiations eventually succeeded. After all, their patience has been seriously tested. The agreement is first and foremost in the interest of the people with the disease and their families.”
In May 2017 both the Netherlands and Belgium decided to end the then ongoing negotiations with Vertex. At the beginning of July Schippers started follow-up negotiations regarding the price of the medicine. Subsequently, the negotiations were stalled when Vertex and Schippers failed to reach an agreement.
Orkambi is a medicine that can be used by some patients with CF. In the Netherlands it concerns approximately 750 CF patients. At the end of 2016 Zorginstituut Nederland noted that the requested price was too high. Due to the recent successful outcome of the negotiations, inclusion in the basic healthcare package is now at last possible. Orkambi is included in the package with effect from 1 November 2017.
Source: Government

Industry invests € 510 million in public-private research
In 2016, Dutch industry invested € 510 million in public-private research projects. The total investments in these projects amounted to € 1,060 million, of which 48% in the form of private contributions. Consequently, an important objective of Dutch business policy, namely € 800 million in public-private investments, has been more than achieved. This is reflected in the Progress Report 2017 – Navigeren met wind in de zeilen. The progress report looks back on the results of the business policy in the past year. Besides the total public-private investments other important milestones have been achieved as well.
Milestones
The Netherlands is innovation leader and the most competitive economy in the EU. On 27 September 2017 it was announced that the Netherlands has maintained its 4th position in the Global Competitiveness Index and has increased the gap with Germany (5th place). A rating in the top 5 is a key objective in Dutch industry policy. Also according to the European Innovation Scoreboard, the Netherlands is an innovation leader and here it ranks 4th as well.
Due to The Netherlands' high-quality healthcare knowledge and great accessibility with the rest of Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) will relocate to Amsterdam. Not only will this strengthen the network of the Top Sector LSH, it will also have a significant economic impact: over 2250 jobs, €150 million direct expenditure and many incoming visitors.
Within the top sectors, scientists, industry and government closely collaborate on groundbreaking innovations and the tackling of societal challenges. Within the Top Sector Life Sciences & Health (LSH) the collaboration RegMedXB has started, which focuses on the cure of diseases like diabetes and arthrosis. At present these diseases can only be treated (care instead of cure). Another collaboration is the organs-on-chips in Human Organ and Disease Model Technologies to improve development of effective and safe drugs. In the past year, the number of public-private partnerships, co-financed by Health~Holland, rose from 22 to 88 and the collaboration with the health foundations has further intensified.
Professor Henk Volberda: "The Netherlands has a world-class innovation-ecosystem."
Regions play an important role in the Dutch competitive strength. Henk Volberda, professor of strategic management and business policy, recently emphasised this with an article in the Financieele Dagblad newspaper in response to the publication of the Global Competitiveness Index of the World Economic Forum: “The Netherlands has a solid foundation. It has an outstanding infrastructure, a good functioning government and a high quality healthcare system. (…) On top of this foundation the Netherlands has also, due to the Top Sector policy and the strong development of regional hotpots (Eindhoven, Twente and Amsterdam) ‘a world-class innovation-ecosystem’.” In the Top Sector Life Sciences and Health this important regional collaboration is strengthened with numerous initiatives. A good example is the platform zorginnovatie.nl where knowledge and information are exchanged.
Business policy
The business policy is directed to all Dutch companies with a focus on a strong entrepreneurial environment and a considerable capacity for innovation of the Dutch economy. Not only the entrepreneur takes centre stage here, but also public-private partnerships. Many of the partnerships take place within the strategy of the top sectors. The top sectors are characterised by high levels of labour productivity, export and R&D investments. With this approach, knowledge institutions, government and industry collaborate on sustainable growth and the tackling of societal challenges.
The value added by the nine top sectors amounted to 145 billion euros in 2015. This is a quarter of the gross domestic product in the Netherlands. Although the sector Life Sciences & Health is the smallest top sector with an added value of 6 billion euros, it has demonstrated the strongest growth of all sectors. Last year the added value in the Top Sector LSH was 25 percent higher than in 2010.
For the complete quantitative foundation of the business policy visit www.bedrijvenbeleidinbeeld.nl.
Stay sharp
The Netherlands has the world leadership with respect to trade and industry. We earn a lot of our money abroad. However, we cannot take our top position for granted. We must stay competitive and there remains room for improvement. Sustainability and digitalisation are not an option, but a necessity. A lot has been done to stimulate interaction with the region, however focused attention continues to be vitally important. Due to strong international competitiveness the Netherlands must continue to innovate and forge ahead.
Read more here:

RegMed XB starring in a popular documentary series Doctors of Tomorrow
The institute for regenerative medicine crossing borders (RegMed XB) has been featured in a documentary series on NPO 1 (net 1, public broadcasting). The progamme is the final installation of a popular series with more than one million viewers about major innovations in healthcare titled Doctors of Tomorrow.
The programme focuses on the solutions for renal failure with researchers Prof. Ton Rabelink and Dr. Marije Koning along with a few patients. Furthermore, type 1 diabetes is also discussed with Prof. Eelco de Koning and a patient. Maarten de Gruyter, Chairman of the DON Foundation and himself a patient with type 1 diabetes, was also interviewed. RegMed XB founder Prof. Clemens van Blitterswijk tells the story about the importance and added value of RegMed XB.
The episode Doctors of Tomorrow starring RegMed XB can now be watch online via this NPO link.
Photographer: Marc Sourbron
Minister opens innovative new hospital in Maaseik
After years of intensive discussions with the users, detailed elaboration of the plans, reconciliation with the assessment authorities and the realisation, the day has come; The new hospital Maas and Kempen is finished. On Thursday 14 September 2017, Flemish minister Jo Vandeurzen officially opened the new hospital in Maaseik that was designed by de Jong Gortemaker Algra architects and engineers.
Hospital Maas and Kempen, previously a hospital with two locations, now has a single new location to the west of Maaseik. A key objective for the design was to make the green environment visible in the hospital. The hospital is not a world in itself. Wherever patients, visitors and staff are they can see the natural surroundings. This enhances the orientation and the tranquility of the users. A second important key objective for the design was the division of the programme into five individual buildings, interconnected with corridors and walkways. This concept strengthens the small scale of the building.
“The limited number of building levels and the division of the programme in five individual buildings provides a pleasant environment for both patients and staff,” says Maurits Algra, architect/director of de Jong Gortemaker Algra architects and engineers
Healing environment
The optimal orientation of the individual buildings with respect to the green environment and sunlight creates a ‘healing environment’. According to Maurits Algra, architect/director of de Jong Gortemaker Algra architects and engineers the limited building height contributes to a pleasant climate: “Even though the project covers an area of 33,250 m², the building never has more than three storeys. The limited number of building levels and the division of the programme in five individual buildings provides a pleasant environment for both patients and staff.”
The five building sections of hospital Maas and Kempen
The hospital functions are divided among the five building sections, as follows:
- Entrance, visitors’ restaurant, and registrations in the ‘Entrance building’
- Nursing wards in the ‘Hotel building’
- Outpatients clinics, administration and management in the ‘Office building’
- A&E, IC, First Aid and Radiology in the ‘Hot floor’
- Facilities from cleaning to laboratory in the ‘Fabric’

FME calls for a National Healthcare Technology Agenda
Healthcare in the Netherlands is among the best in Europe. To make sure it stays that way, we have to tackle the healthcare societal challenges together: too few people work in healthcare and a growing number of people need healthcare. Smart technology offers the solutions that improve the quality and affordability of healthcare.
FME chair Ineke Dezentjé Hamming-Bluemink: “Technological innovation makes treatments more reliable and precise, and gives the healthcare professional space for what actually matters in healthcare: attention for the people. That is why it is time for a National Healthcare Technology Agenda.”
Until now there was no clear picture of the position healthcare technology holds in our hospitals. That is why the healthcare branch in the FME (the Dutch employers' organisation in the technology industry which brings together 350 technology companies that want to improve healthcare) commissioned research bureau Ecorys to map the value of healthcare technology in the Netherlands and give recommendations for the future.
The research shows: of the €83 billion we spent on medical and long-term care in the Netherlands, €3.2 billion was spent in hospitals in 2016 on healthcare technology (€2.9 billion for consumables and €0.3 billion for medical equipment). This is 13% of all expenses in Dutch hospitals.
Text continues below the picture
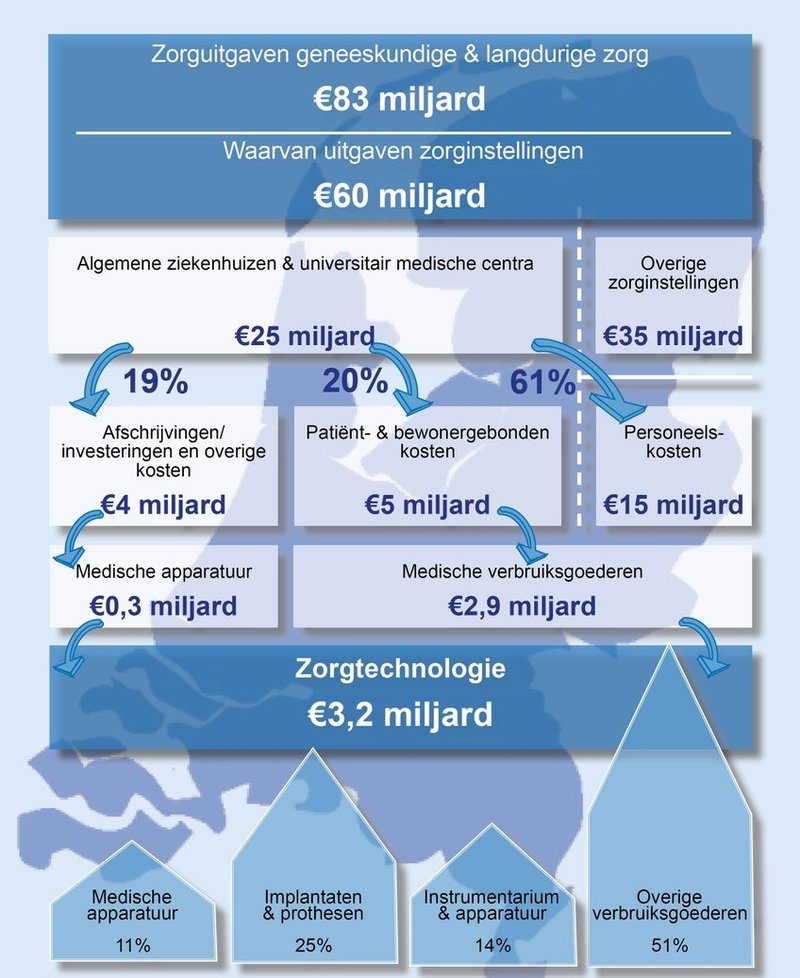
FME views this study as a start to improve healthcare in the Netherlands and to create a National Healthcare Technology Agenda. FME chair Ineke Dezentjé Hamming: “Our offer is to take on this challenge with the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport, patient organisations, healthcare providers and insurers. The new coalition agreement is based on: good healthcare for everyone in the right place at the right moment. I wholeheartedly agree with this! Wouldn’t it be fantastic to work together on a National Healthcare Technology Agenda? Together we can speed up the movement towards value-based healthcare.”

Building on Cures Act, FDA lays out cell therapy fast track in regenerative medicine framework
The FDA has created a policy framework for cellular therapies and other regenerative medicines by releasing two draft and two final guidance documents. Publication of the texts builds on the 21st Century Cures Act by setting criteria for the new Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation and outlining the benefits of the regulatory status.
Given two of the documents are finalized versions of existing texts and a third seeks to simplify the regulation of devices that enable regenerative treatments, the RMAT guidance (PDF) is the novel part of the framework for drug developers. In the guidance, the FDA takes the RMAT status created by the 21st Century Cures Act, contextualizes it against other regulatory designations and explains how and why companies may want to apply.
“With the policy framework the FDA is adopting a risk-based and science-based approach that builds upon existing regulations to support innovative product development while clarifying the FDA’s authorities and enforcement priorities.,” says FDA commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D.
RMAT is open to investigational regenerative medicine therapies that treat, modify, reverse or cure serious conditions and have generated promising preliminary clinical evidence of efficacy. The FDA cites a single-arm, open-label study of a skin burn cell therapy and a phase 2, dose-finding trial of a heart failure regenerative medicine as examples of the types of experiments that could provide preliminary evidence of efficacy.
Candidates that receive RMAT status will receive all the benefits of the FDA’s fast track and breakthrough designation. The law that created RMAT also covers accelerated approvals and how to satisfy the subsequent post-approval requirements.
The FDA is accepting comments on the RMAT text and draft device guidance for 90 days.





