Public Private partnerships
More examples on Public-Private Partnerships
Some detailed examples of public-private partnerships of the last period to get inspired by.
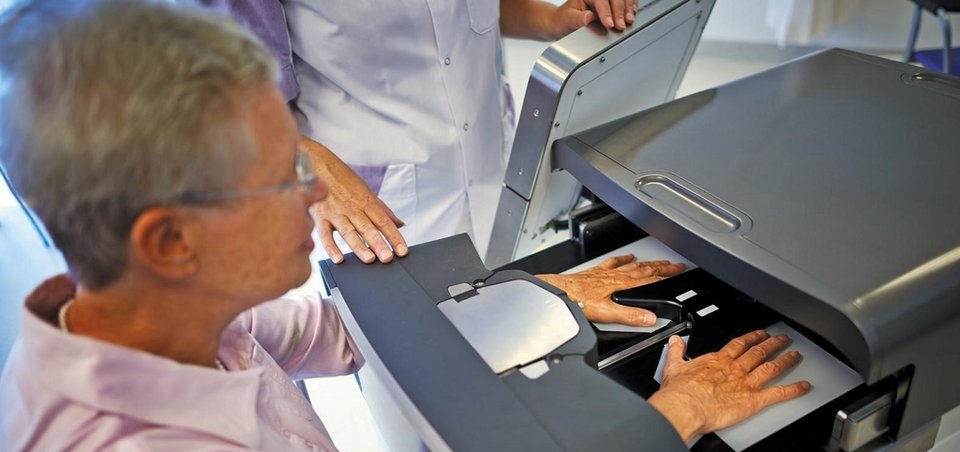

HandScan Hemics: painless and objective examination of patient's arthritic hands
Read more ›

Faster registration of new drugs by label free human mass balance studies
Read more ›
A study on the Sigmascreening’s Sensitive Paddle for mammograms confirms potential health benefits
Read more ›
Better care for the elderly in Singapore through Dutch game
Read more ›

HandScan Hemics: painless and objective examination of patient's arthritic hands
In the Netherlands, approximately 100,000 patients suffer from rheumatoid arthritis. The medical examinations are now performed manually by the rheumatologist: the inflammations and swellings are assessed by squeezing and feeling the patients' hands. Needless to say, many patients experienced this as a recurrent torment. The medical device company Hemics now provides a new supportive, non-invasive and fast method for rheumatologists.
The HandScan, developed by the Philips spin-off company Hemics, aims at making these painful examinations obsolete. The device is user friendly: the patient inserts his or her hands through pressure cuffs and places his or her hands on a translucent handrest. The pressure cuffs around the lower arms are inflated for a short period of time to modify the blood flow in the hands. In tandem, the hands are illuminated to measure the speed and magnitude of blood pooling, an indication of inflammation. The HandScan hereby supports the rheumatologist in objectively assessing the disease activity in a fast, safe and painless way.
The Maxima Medical Centre in Eindhoven is the first hospital in the world to commission the device, as the MMC was closely involved in its development. In the UMC Utrecht a study is furthermore set up to examine the cost efficiency and the efficacy of the HandScan. This study is financed by the Dutch Arthritis Foundation (reumafonds) and the Top Sector Life Sciences & Health through the LSH Impulse allowance. In the coming period the HandScan is expected to become available in at least six other medical centers.
Hemics furthermore aims to broaden the use of the device. A variant of the HandScan that scans the inflammation in the feet is already on the drawing board. Besides, the implementation of the device for other diseases, such as osteoarthritis, is reflected upon.

Faster registration of new drugs by label free human mass balance studies
Great example of a public-private partnership funded by Health~Holland
In collaboration with four partners from the pharmaceutical industry, TNO aims to develop a sensitive AMS (Accelerator Mass Spectrometer) method for the generic detection of drug compounds present in human matrices and hereby aimed to speed up drug development by conducting label-free mass balance studies rather than 14C-labelled compound.
For registration of new small molecule drugs, human mass balance studies are required to substantiate that the fate of the drug is thoroughly understood. These mass balance studies, normally executed with 14C labelled drugs, are high cost studies and are therefore generally in the critical path to registration. However, a labelled drug is not necessary for all commercially available drugs. For a specific selection of compounds under development it is possible to execute mass balance studies without any additional label, and suddenly for these drugs, any human clinical trial would become potentially a human mass balance study. This would save a tremendous amount of costs and time, and, more importantly, this would take the human mass balance study out of the critical path. Time to market would be shortened by up to one full year.
Within this project, the partners investigate the possibility to analyse drug compounds, that meet the criteria for this innovative approach, in physiological fluids (urine, plasma, faeces) in the low pg/mL range by Accelerator Mass Spectrometer (AMS). Currently there are no generic analytical techniques available that could provide mass balance data directly from any clinical trial with unlabelled compounds.
This project will result in a proof of concept, for both technical (AMS tuning) and analytical (sample preparation) aspects. If successful, it will result in generic methods, qualified according to European guidelines, which can be used in clinical studies.
See website for more information.

Better care for the elderly in Singapore through Dutch game
In April 2016 the Holland Innovation Network of the Embassy of the Kingdom of the Netherlands organised an innovation fact-finding and matchmaking mission to Singapore. Subject: Integrated care and care for the elderly. Just one year later, the first deal is a fact. Sengkang Health in Singapore has purchased 500 licenses for the serious game Delirium Experience, in order to train their doctors and nurses in delivering better care to patients with a delirium.
“Care for the Elderly is a global challenge. This is a fantastic first step towards international cooperation." said Prof. Dr. Sophia de Rooij, internist and initiator of the Delirium Experience.
The Delirium Experience is an online interactive video game that allows caregivers to learn, in a ‘playful’ environment, how to better recognize and treat a delirious patient. A delirium, also referred to as acute confusion, usually occurs in the elderly as a result of a physical disease. This type of confusion is temporary, but due to the severity of the symptoms, a patient is often confronted with powerless and even non-empathetic hospital staff and family members. The Delirium Experience wants to contribute positively to gaining more knowledge on this subject, but also to improving skills and attitudes, which will enable physicians and nurses to take even better care of this category of patients who are often viewed as ‘complex’.
“Care for the elderly is not only a problem in the Netherlands. It’s precisely the scalability of applied games to a wide range of target audiences and countries that insures the high potential impact of this kind of game. That is why we translated the game into English last year and that is now really starting to pay off." says Sophia de Rooij.
The 500 licenses have been purchased for use by both nurses and doctors from Singapore. The first trainees will have started this new way of learning by this summer. “We find the game exhibit a great actual and realistic video portrayal of patients' perspectives and what they experience. It’s very experiential to allow healthcare providers to ‘see’ through the patient’s point of view. We believe this enforces more positive behaviors and perception towards caring for these patients, instead of simply brushing them off as ‘difficult’.” Says Dr Melvin Chua, Head of Department of General Medicine, Sengkang Health.
The game has been developed by IJsfontein, leader in the Netherlands in the field of applied gaming, in collaboration with the Foundation for Effective Care for the Elderly and the University Medical Center Groningen. The Delirium Experience is available on a licensed basis. More information can be found at www.deliriumexperience.nl. By this summer, the Delirium Experience will be expanded with a teaching package and a test for which accreditation will be obtained.


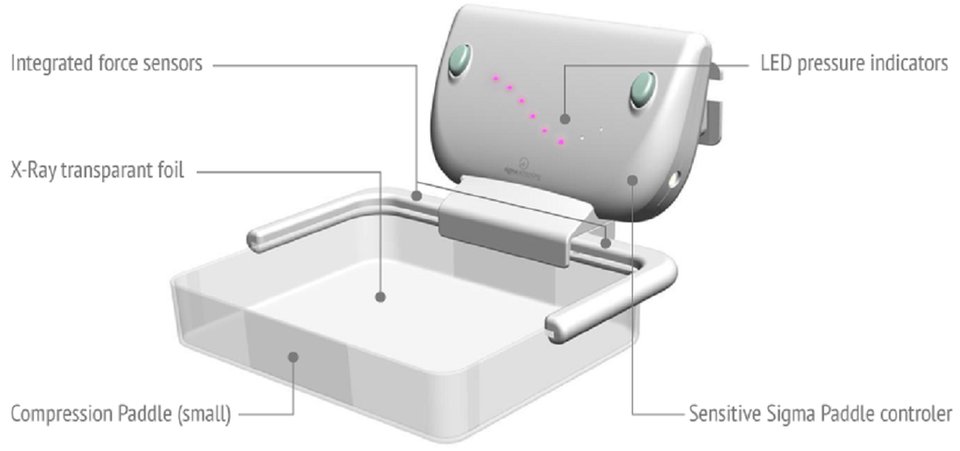
A study on the Sigmascreening’s Sensitive Paddle for mammograms confirms potential health benefits
Fewer false positives, fewer false negatives and reduced unnecessary pain
Sigmascreening, a Dutch MedTech developer and world leader in the field of pressure based digital mammography and breast cancer screening, announces that a large independent Norwegian study further confirms Sigma’s hypothesis that pressure has a clear relation with the most optimal results in mammography. The study confirms the importance of pressure in accordance with Sigmascreening’s concept of the Sensitive Sigma Paddle, which applies pressure guidance during mammography. The combination of results of an earlier Dutch and this new Norwegian study shows an optimal pressure in the range of 10 kPa. This pressure clearly correlates very well with the proposed pressure by Sigmascreening.
The data show that high breast volume and low compression pressure are associated with positive performance measures such as lower recall rate and higher specificity (true positive) of tumor detection. Procedures with too low pressures result in unnecessary recalls due to false positives. Flattening of the breast on the basis of pressure, also prevents unnecessary discomfort and pain, which may contribute to a higher breast cancer screening compliance of women. The Sigma pressure technology aims to optimize these three elements.
Sigmascreening’s Sensitive Sigma Paddle is the first pressure based compression paddle providing real-time and reproducible information on mammographic pressure, which can considerably reduce frequently experienced pain for women during screening. It optimizes compression for every individual breast, taking into account breast size and tissue stiffness, which leads to an optimal mean contact pressure per woman thereby optimizing both specificity (true negative) and sensitivity (true positive) for the most optimal screening result.
Ivo Aarninkhof, Sigmascreening’s CEO, says: “We strongly believe that our less painful solution will increase the compliance of breast cancer screening programs, while at the same time significantly improves the diagnostic performance.”
Rapid market acceptance in Europe
Sigmascreening’s pressure-standardized breast compression is expanding rapidly in screening centers and hospitals throughout Europe. In Europe, over 10,000 patients already experienced the more woman-friendly way of making mammograms while clinicians are starting to recognize the improved sensitivity and specificity of our technology. The Sensitive Sigma Paddle with CE marking is already being used in the United Kingdom, Norway, France, Germany, Sweden, The Netherlands, Belgium and Switzerland.
Source: Sigmascreening
